News & activities
 News releases
News releases
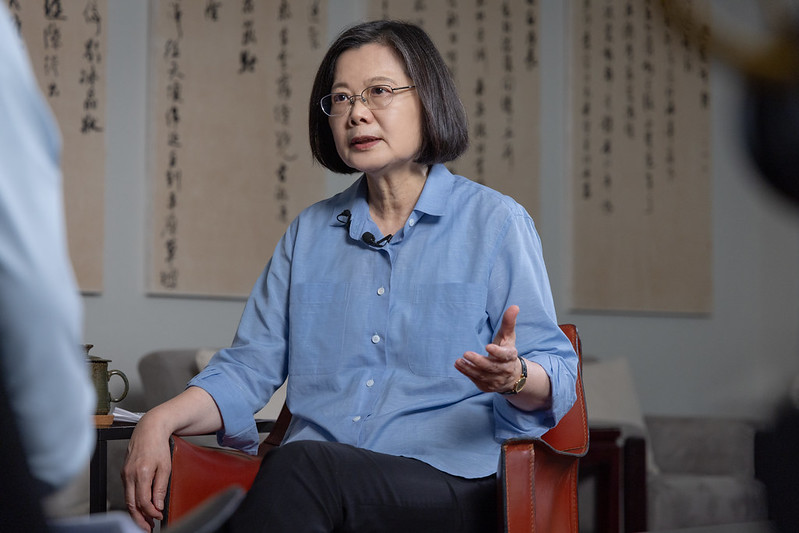
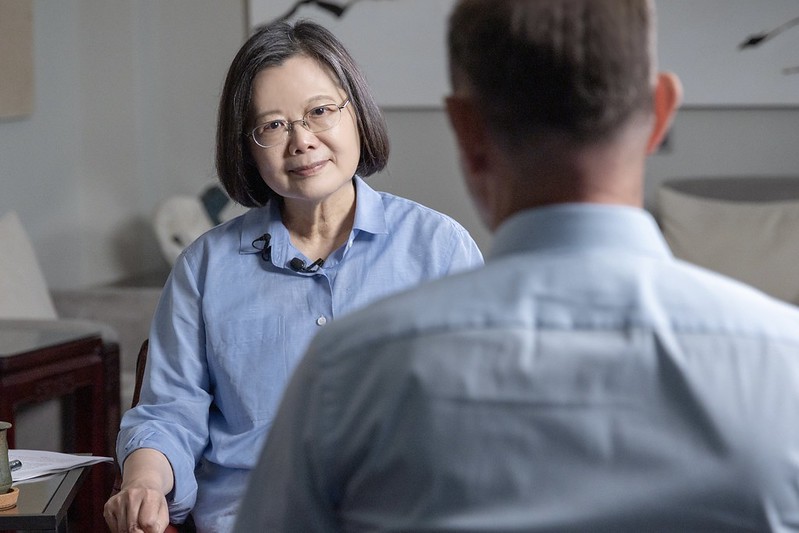
In a recent interview with the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC), President Tsai Ing-wen responded to questions regarding women’s participation in politics, marriage equality, Taiwan’s COVID-19 response, the cross-strait situation, Taiwan-US relations, the impact of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine on Taiwan, global supply chains, and her achievements during her time in office.
Following is the text of the questions and the president’s responses:
Q: You are the first female president elected here in Taiwan. That obviously makes you something of a transformational figure in Taiwan politics. So what do you think, in your own mind, are your most important achievements during that time?
President Tsai: Let me say this first: people thought that was something unusual happening in Taiwan, but I want to say that the Taiwan society and democracy nowadays are mature enough to produce and accept a woman president, and that is a tremendous achievement of the Taiwan society. In these eight years you have [the] US-China trade conflict, you have wars, in Ukraine and recently in Israel as well, and also, you have the pandemic, as well as the increasing tension in the region because China has become more aggressive and assertive. So this is a time of changes and challenges. And being a president at this moment in time is pretty challenging, I must say.
Q: You’re saying Taiwan is able to accept a female president. I mean, this is still a very patriarchal society. You have appointed many women to high positions in government. You have appointed the first transgender cabinet minister in Taiwan’s history. Do you think there’s an enduring legacy there that will last? Or is there a danger Taiwan could revert to what I might call the boys’ club once you’re gone?
President Tsai: I do a lot of adjusting about that boys’ club. But this is an immigration society. People came to Taiwan at different times. And we also have the indigenous people here. So in an immigration society, there are a lot of challenges, and people are less bound by the tradition and the established practices because they are in a entirely different and sometimes very unfamiliar environment and they have to survive in all of this in the environment. So they are less bound by the traditions. And the main goal is to survive. And they have to help each other and be more accommodating. This is why we have been able to overcome all sorts of difficulties and move from the authoritarian age to [the] democracy that we have today, and we move ourselves from the traditional practices of marriage and also the faiths associated with it, to now that we are accepting same-sex marriage. So it’s the people here, and the people who came here at different times, and they learned to survive in an entirely different environment.
Q: So you’re saying basically that means Taiwan is a more open-minded society than, for example, China is?
President Tsai: We have the potential of being an open society, and the fact is that over the years we realized its potential and [have] become, in my view, an advanced society.
Q: You talked a little bit about same-sex equality in marriage here. But you were well ahead of any other country in Asia in pushing through that legislation. Why was that such an important priority for you?
President Tsai: Because that’s the hope [of] the younger generation, because that is a way to express ourselves as a more advanced country in terms of the progressive values. And also we have very active advocates for the same-sex marriage here. And it’s a test to the society here to see to what extent they can move forwards with their values. And it was a very difficult journey for us to travel through, to get to the stage that the legislature finally approved the same-sex marriage. So it has taken a lot of efforts and a lot of people’s contribution as well. And I am actually rather proud that we managed to overcome our differences and get together and produce a package that we can all live with, and eventually we are all proud of.
Q: You mentioned also another thing that, as a success for Taiwan was his handling of the COVID pandemic. And the statistics are truly remarkable. That’s a tremendous achievement in an open, democratic society where you can’t use draconian measures to lock people down. There’s one thing that’s very noticeable. Although you didn’t have any lockdowns domestically, you did close your borders very quickly. Was that the key?
President Tsai: That was one of the keys, because of the SARS experience. And the source of the disease back then was from China. And this time our suspicion is that it is also from China. So we make a very quick decision and then stopped the Chinese tourist groups coming into Taiwan. And that was a time very close to the Lunar New Year. But we made the decision. And it was quick and early enough.
Q: I’m going to move on to sort of the big challenge that faces, has faced, you over the last eight years. And that’s the threat from China. A lot of people don’t really know what Taiwan’s status is around the world. Some people, you know, China claims that Taiwan is part of China. Most people here in Taiwan, when you look at surveys and you ask them, they say, we want to maintain the status quo. No unification, no independence, status quo. What is the status quo mean for you?
President Tsai: I think all the people agree on this thing, that we are on our own. We make our own decisions. We have a political system to govern the place, and we have [a] constitution, we have laws regulating the society as a whole. And we have our military. So we have all the elements of a state. And it’s just that we don’t have enough number of diplomatic recognitions from other countries. But when [the] time comes, people may want to say yes, let’s move forward and let’s establish some sort of diplomatic relations with Taiwan. And China, of course, would say that we’re part of them, and they’re trying to use the UN resolution of the early 1970s, but a lot of other countries have different views because that doesn’t cover the future of Taiwan. So, it’s for the people to interpret what Taiwan represents at this moment in time. But the most important thing is that we are on our own, and we are a democracy, and we enjoy freedom and democracy and progressive values, and we are a group of people that are very proud of ourselves.
Q: Do you fear Xi Jinping? Do you think the world, the democratic world, should fear Xi Jinping and his ambitions?
President Tsai: Not to the extent of fear, but we have to be very careful in the development of China, because China is a source of uncertainties for the rest of the world. Of course, it’s a military power, but it has reached a stage where they are actually short of new momentum for its economic growth, and that has serious consequences for the Chinese society. So China has its own problem to deal with at the moment. And the world today, after the Ukrainian war, seems to be more united, especially the democracies are more united than before, to form some sort of deterrent against a possible expansion of China in this region and the rest of the world. I think Xi Jinping now, despite the fact that he may have a plan of some sort, but I don’t think that is a definitive plan because the world is changing, the situation in China is changing, he has to revisit his plan from time to time to see whether there’s any adjustment needed. But the world is very different now, especially after the Ukrainian war, because the democracies seem to be able to get together to form a meaningful deterrent whenever there is an invasion contemplated. So, I think if we deal with the matter very carefully, there’s still a great possibility for us to maintain peace as we all need.
Q: One of the things you’ve done very differently from your predecessor: He engaged in dialogue with China. He was trying to get Taiwan into, basically, an economic partnership with China. You, when you came to power, decided on a very different course, it strikes me, one of firstly, building up Taiwan’s own military strength. Is Taiwan stronger and more secure now than it was eight years ago, and if so, how?
President Tsai: Responding to your question, I would say that the military capability of ours is much strengthened with the investments that we have put in in the last eight years and also with the assistance of our friends, primarily from the United States. So the investment that we have put into the military capacity building is unprecedented, despite the fact that people are urging us to increase the budget further. I think if there’s a need, we will always increase and expand our military spending, but this is the time for us to use the money available efficiently to build our capacity at a speed that can match with the expansion of the Chinese military capability.
Q: I suppose your critics would say, this is all good, but ultimately Taiwan is small. It has a small population compared to China, and China’s military is vast, its military modernization is extraordinary. And that in the end – this is what your critics would say – Taiwan cannot hope, by itself, to deter China militarily. And so your policy of building up the military is sort of futile, because of the huge discrepancy in power.
President Tsai: Of course that makes some sense, but in reality people are talking about whether a place is dispensable in relative terms. The cost of taking over Taiwan is going to be enormous, and Chinese leadership have to make a good calculation as to whether they are prepared to pay the cost. But what we need to do is to increase the cost of an invasion. Strengthening our military capability is one. And working with our friends in the region to form a collective deterrent is another. But [China] has become so aggressive and assertive in recent years. A lot of other countries in the region are alert and they to an extent some of them may have a conflict with China at sea. And so China is not an issue for Taiwan only. It’s an issue for the region, and it’s a concern for a lot of countries in the region as well. So people get together to express their concerns and they say very clearly that there should be no unilateral change of status quo, and [that] peace and stability is the most important thing for the region and for the world as well. That has become a consensus of some sort.
Q: Suppose again, just playing devil’s advocate here, your critics would say, well, that’s all very well, but Taiwan has but very few formal diplomatic allies. It doesn’t have any formal military alliances. And that during the last eight years, particularly the last four years, the situation around Taiwan has actually become objectively more threatening. Every day we see Chinese PLA aircraft flying into Taiwan’s air defense identification zone. We see Chinese Navy ships coming across the median line. So the threat environment during this period seems to have gotten worse.
President Tsai: Of course, we cannot exclude any possibility at the moment, including a possible military conflict, an invasion from China. But the thing is with the collective efforts of the parties concerned in the region, China actually feels the pressure. Because it’s not only [the] military [that] is a concern. They have to be aware of the fact that a war may cost their economic development, and the economic consequences [are] such that it may probably delay the development of China for years, even for decades. So if you are a leader of China, what is more important, taking over Taiwan or your continuing growth economically and socially?
Q: You talked about America being Taiwan’s friend. Clearly it is. President Biden has been extremely supportive of Taiwan. When asked about whether he would intervene if Taiwan were attacked, he has repeatedly said yes. His critics have said that that is moving America too far away from this idea of strategic ambiguity and that actually, that makes the situation for Taiwan more dangerous. What do you think?
President Tsai: I think the US administration has been very careful in delivering the messages they want to deliver to the public. So as far as I’m concerned, the way I read it is that the ambiguity is still there.
Q: And I know I was here when probably the most high-profile American visit during your presidency was that of the US House Speaker Nancy Pelosi. It caused a big reaction from China. For the first time, China fired ballistic missiles over the top of Taiwan into the Pacific Ocean. So I wonder, from your point of view, what are the benefits of these sort of very high-profile visits? Are they just a sort of somewhat empty gesture? Or is there something really concrete that they bring for Taiwan because they seem to cause a lot of trouble for you as well.
President Tsai: For any president of Taiwan, you’re not in the position to say no when your friends want to come and show support to you. We have been isolated for a long time, and we need friends, and we need people to come and express their concerns for us. So for any president, you just can’t say no to a visit like Speaker Pelosi’s. But the thing is that, of course, there are risks associated with it, so you have to manage the risks. There are a lot of communications and diplomacy, the details of which I cannot tell you, but there [was] a lot of work behind the scenes to make it less of an impact on the cross-strait situation.
Q: How important is victory on the battlefield of Ukraine and continuing Western support for Ukraine in terms of how it affects Taiwan?
President Tsai: Many people suggest that Taiwan is a much [more] important case than Ukraine because we are indispensable in terms of global supply chain, and our geographic location represents a great deal in terms of strategic values to the region as a whole. And there are arguments that perhaps the US should shift their support and resources from Ukraine to Taiwan. We say, no, you have to support Ukraine until the very end because the determination is the most important thing as far as we are concerned. We don’t want to take advantage of the Western countries deciding to reduce or eventually abandon the Ukraine. No, that’s not our position. Our position is that the democracies should support Ukraine with all force and effect because that is a very important element in terms of building confidence here in Taiwan.
Q: You mentioned Taiwan’s position in the global supply chain. Do you think there’s now a much wider recognition of just how important – and we’re talking here, of course, we’re talking about semiconductors, right? We’re talking about Taiwan semiconductors and other big Taiwanese companies. Do you think people around the world understand how vital Taiwan’s position is?
President Tsai: Let me put it this way: 90% of the advanced chips are produce in Taiwan. For the future technology like AI Taiwan holds the key. So that itself is important enough for the rest of the world. And geopolitically, you have Taiwan here, stand[ing] very firm against the possible aggression from China. That is a good demonstration [of] how a country can protect itself from invasion with strong determination.
Q: We’re going back to a sort of legacy question, but it’s not so much about big politics, but about the sort of society and environment. I mean, what is it that you think of that makes you feel satisfied about how Taiwan has changed in these last eight years?
President Tsai: I think we’re more international now. We have lots of friends outside of Taiwan. We used to be rather isolated and the primary relationship that we have to manage is with China. But nowadays we have to manage a lot of other relationships with the rest of the world. And we interact directly with a lot of other countries and we help each other, and we have trade and investment relationships.
This is a time that we feel that we are actually part of the world rather than part of the cross-strait. And so I am actually rather pleased that we are now a Taiwan of the world, that is, probably, if you want to say achievement, one of the achievements I’ve got.
The other thing is that I actually made this place a better place to live, in the sense that now, Taiwan’s economy is one of the most competitive in the world. And our technology level is, again, it’s very impressive and to the extent that a lot of people feel that Taiwan is indispensable to the world’s supply chains. It’s not limited to semiconductor. It’s to others as well.
And I have carried out reforms, so that we now have a more financially sounder pension systems, the pension plans for the public sector employees, as well as [for] the other types of pension plans here. I have helped improve the finances so that people do not have to worry that much about the financial sustainability of their pension plans here.
The other thing is the military reform. We made our military a more modern one, a more resilient one. And I was actually able to convince the public here that extension of the mandatory military service is something that we need to do, and I get the support of the people here. And also the young people, despite they have some complaint, but it’s not about their love for their country. They have love for their country. They have the dedication for their country. And they have no hesitation to serve in the military. It’s just that we have to make sure that their time spent in the military is worthwhile. We are obligated to provide them with the best equipment, best training, and they know how to protect themselves as well as protect the country. This involved a lot of work. But what is more important is that I work with the military so that we, in the process, are building what we call an all-of-the-society defense system here.