News & activities
 News releases
News releases
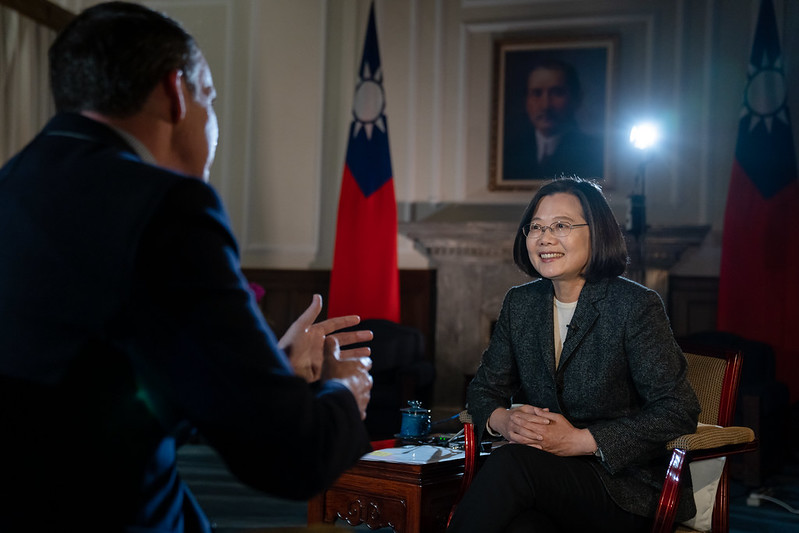
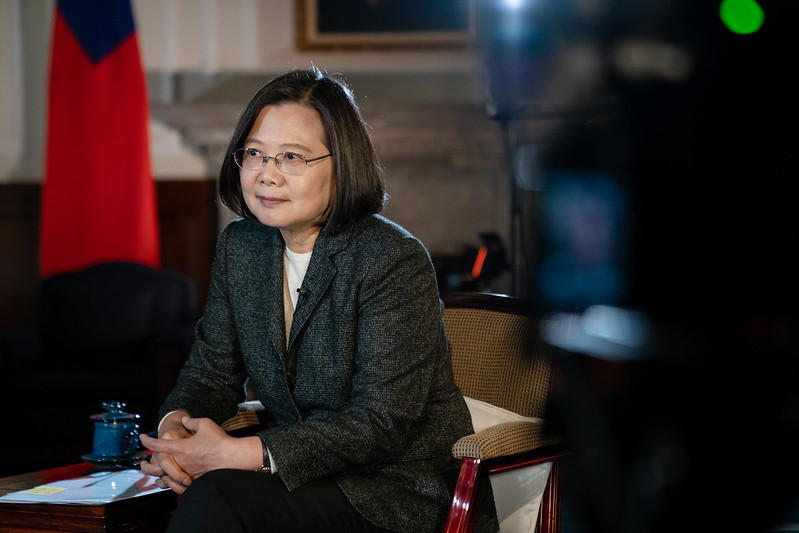
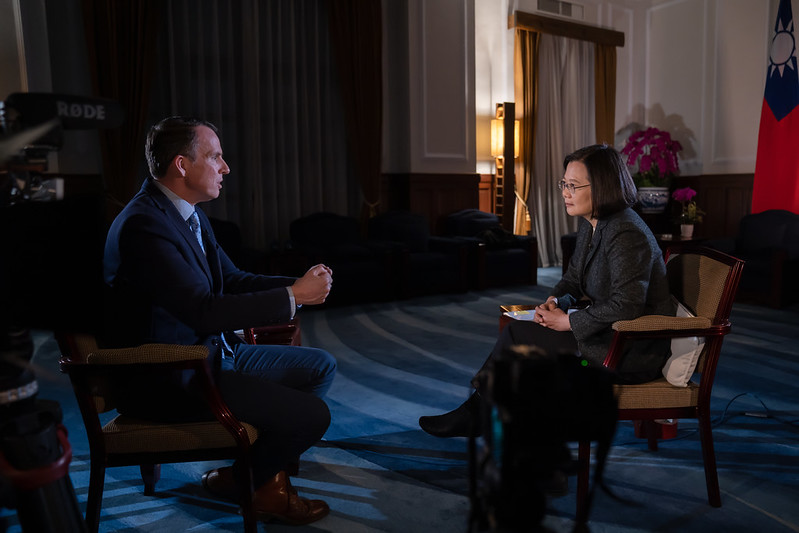
President Tsai Ing-wen was interviewed by the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) on January 14, and she responded to questions regarding issues such as our presidential election, cross-strait relations, Taiwan-US relations, national defense, and diplomacy.
The following is the text of the interview:
Q: If we leave aside the question of timetable, the question of practicality, are you in principle, at least, in favor of the idea of formal Taiwanese independence?
A: Well, the reality and what it is now is that we are already a functionally independent country. And we have our own government, we have our own elections, of course, presidential election, and that is a way to express that we do have sovereignty, and our people elect their own leaders. So, effectively we are a country already.
Q: Will there come a day when that reality needs to be spelled out by calling Taiwan a country, and a formal declaration of independence to do that?
A: Well, the idea is that we don't have a need to declare ourselves an independent state. We are an independent country already and we call ourselves the Republic of China (Taiwan), and we have our own system of running the country, and we do have a government and we have a military, and we have elections, like the presidential elections that you have witnessed.
Q: Your victory is largely put down to the central position of China in the campaign. Why do you think China was such an issue for voters?
A: The election is not only about China. It's about a lot of domestic issues, and also a lot of sort of choices of values. So I think, of course China played a significant role in this election, but at the end of the day the president or the contenders for the presidency have to show that he or she has the ability to run this country as a democratic country, and also has the ability to manage the economy here and to make us more competitive economically. And also, the president, the candidate, has to prove that he has the ability to take care of everybody here, to make sure that there is equality here. So there are a lot of things that the people are expecting from the next president. So you have to come up with a sort of, you have to settle on policies that make people feel that this is the leader they want for the next four years. And of course, China is one thing, because people want to make sure that the president can deal with China in the right way, so that we will be able to keep our separate identity, and we will have our own sovereignty, and that we get respect from the rest of the world. And also at the same time, the president has to have the ability to manage the relationship so that the relationship can be kept stable.
Q: Some people would say China has always been a threat in the background. Why was it so different this time round?
A: Because over the last three, more than three years, we've seen that China has been intensifying its threat. They have all sorts of actions, military exercises, and they have their military vessels or aircraft cruising around the island. And they also have quite a number of things that are much more drastic than before. So the intensity of the threat is increasing, and also with the things happening in Hong Kong, people get a real sense that this threat is real, and is getting more and more serious.
Q: Your predecessor, Ma Ying-jeou, was able to preserve Taiwanese democracy whilst building stronger ties with China, economically and culturally. At a small price, the continued ambiguity over the status of this island, what's not to like about that approach?
A: The situation has changed. The ambiguity can no longer serve the purposes that it was intended to serve. So, we're facing a very different situation now and the type of ambiguity that the previous governments wanted to use to preserve some sort of space for both sides is no longer there. And this is the time for us to think about this situation—the people's expectations, the changes in international politics, and also the potential regional tensions. So "cross-strait" is no longer cross-strait relations per se. It's part of the regional situation. So it's a much more complicated situation now.
Q: There's also been talk by your party about the dangers of Chinese influence. Doesn't your landslide victory, though, suggest that those claims were overblown?
A: Well, I don't call it a landslide victory as much as a convincing one. But not to the extent of a landslide. We learned our lesson from the last elections, which were local elections. In that election, fake news, bad rumors and a lot of other things influenced the people's perception here. And as a result, we suffered a lot from that election.
Q: So you've no doubt that's coming from China?
A: Yes. To a large extent, yes. And therefore after the election we had a review of the whole situation, and we have come up with a system to strengthen the government's ability to clarify things. We have also amended quite a number of laws to hold people accountable if they are distributing fake news or manufacturing fake news.
Q: Critics are worried that that in itself could be used as an attack on free speech.
A: Yes. And we will do it very carefully so that we keep the right balance, and while people are reminded that they shouldn't be doing all these bad things, at the same time they get protection for whatever they want to say as a free citizen.
Q: You don't buy the idea that reverting to the old compromise that being more ambiguous about Taiwan's status could take us back to a golden era?
A: This situation is very different. I do think that both sides have to think more seriously about the future, so that we can work to find a way to co-exist, and maintain peace and stability across the strait.
Q: You spoke about the rising threat from China. How serious in your view is the risk of war today?
A: You cannot exclude the possibility of a war at any time. But the thing is you have to get yourself prepared and develop the ability to defend yourself. But in addition to this military preparedness, what is more important is that you have to get international support for your cause. So, we have been adopting this attitude of non-provocation, because we don't want to be the party provoking the other side, and make the situation worse or give the other side the excuse to take whatever action they want to take. So we have been pursuing this non-provocative approach, and to a certain extent, we're rather mild in our response, in our view, toward their provocative actions.
Q: Is Taiwan ready to defend itself? Do you believe you would be able to stand up to a military action?
A: We have been trying very hard and making a lot of efforts to strengthen our capabilities. I do think we have pretty decent capabilities here, and invading Taiwan or trying to invade Taiwan is something that is going to be very costly for China.
Q: And are you confident that were that worse-case scenario to arrive, the United States would come to your aid?
A: We have been working with our friends in the region so that we have a coordinated effort to maintain peace and stability in the region. So what we intend to do is continue our efforts with them so that peace and stability can be maintained.
Q: And as you take this stance and shift away from China's sphere of influence, and try to build alliances and strengthen your alliance with America, some people would say where's the real dividend? There's still no sign of a free trade agreement with the United States—that seems as far off as ever. The possibility of losing some of these economic ties with China, as it punishes you for your stance—isn't there a risk that the result of all of this will be economic harm?
A: At any time of change, there is always risk and also challenges, but opportunities as well. I think so far we have been okay in the sense that we have utilized this situation to our benefit. Because of these changes, we are actually given a lot of opportunities.
I can give you an example. With this trade conflict between China and the US, a lot of our investors in China are now coming back to Taiwan. We encourage them to come back.
When they come back and establish their capability here, it is all state of the art and also high-end manufacturing capability. This will bring a sort of momentum for our economic growth for the next stage. The opportunity is to complete links with Taiwan and we are trying to maximize the benefit of this opportunity. With this flowing back of investment from China, our economic outlook looks better than people generally expect.
Q: Talk to me a little bit about your election victory. Some people are suggesting it's not just the bigger questions, it's the immediate strategic challenge from China, but something is changing in Taiwan, particularly the younger generation and that question of identity.
A: I think the young generation are pretty used to the idea that we have a separate identity and we are a country of our own. So if there's anything that runs contrary to this idea, they will stand up and say, "That's not acceptable to us." When they experience the situation in Hong Kong, they have this sense that the threat from China is real and is serious. They have to come out and express what they feel about it. And they think the best way to express their feeling is to go and vote.
Q: You have no doubt that under the "one country, two systems" formula Hong Kong's freedoms are being eroded?
A: Yes, I think so. There was a time, in the past, that the people here were very envious of the Hong Kong people because they had this amount of freedom under British rule. But after 1997, things changed a lot. As we have all witnessed in the recent events, yes, when the police are taking action against the Hong Kong people—the protestors—people really think that this is something they don't want to see and it's not the police a society should have.
Q: How do you expect Beijing to react to your victory?
A: They should engage in serious thought about the people's expectations as expressed by the election result. This is a very strong message from the people of Taiwan. They don't like the idea of being threatened all the time, and they don't like the idea of being undermined all the time. We're a proud people, and have success in every aspect of our lives. We're a successful democracy and have a decent economy. We deserve respect from China. So I think that China should give very serious thought to what the people here want to say through this election.
Q: You spoke after the results about your hope that there could be a return to dialogue. How do you begin? What could you offer Beijing that might, in your view, open that door a little?
A: I think for the Chinese to sit down and think and also have this preparedness to face the reality. That is the key. If they're not prepared to face the reality, whatever we offer won't be satisfying to them.
Q: I think you're at 15 [allies] now. Do you expect it to stop there?
A: No, the Chinese will definitely not stop trying to take away our diplomatic allies. But we will try to do whatever we can to keep our diplomatic allies.
Q: Without an expression of good faith on your side, and this is what your critics say, you in a way are inviting China to react in the way that it is?
A: No, I think that building trust is something that is needed. But I've been President of this place for more than three years. I have been rather reasonable in terms of managing our relations with China, and we have refrained from doing things that might be considered as being provocative to China. We have adopted the approach of maintaining the status quo despite the fact that there is so much pressure here that we should go further. But, for more than three years, we have been telling China that maintaining the status quo remains our policy. I think that is a very friendly gesture to China.
Q: Do you feel a certain responsibility in terms of some of those softer issues? In particular, for example, your success in getting through the Marriage Equality Act--hugely symbolic. Do you see that as, perhaps in the end, your biggest legacy?
A: No, I think I've done quite a few things that people will eventually realize are good for the country. For instance, the pension reform, which of course was a very painful process to go through. But at the end of the day, we do have a pension system for public sector employees, and they can be assured of their retirement payments without worrying about the bankruptcy issue. And of course, the same-sex marriage issue is something that was initially very divisive here, but again, we went through a very painful process to get there. And then we are trying to do a lot of things to reform the judiciary here, to make the system more credible. But it's a much, much, much bigger challenge and requires more time, but we're in the middle of it. So hopefully, we'll be able to do things fast enough so that by the end of my second term we will have concrete results. And green energy is something we have placed a lot of emphasis on. We have offshore wind farm projects, which are going to make the energy supply cleaner, and also we will be building an industry that is related to this wind power. We will be the first country in Asia with that capability. So we are actually doing a lot of things that are not traditionally things Taiwan would do, but we're doing them.
Q: In four year's time, what's your vision?
A: I want to make this place more democratic, and in terms of the economy, much more competitive, one of the main economic players in the world. Also in terms of progressive values, we have been doing quite a few things, which eventually will make Taiwan the most progressive country in Asia.
Q: Abolition of the death penalty?
A: That is a difficult issue to deal with.
Q: What would you support?
A: That is perhaps a goal people always want to achieve. But the thing is that it is not supported by the majority of the people here. That requires a long process, a long time, to change the mindset of the people here. And actually, in a democratic society, you need people's acceptance of these ideas before you can make a move. And so, until people have enough confidence, feel comfortable about it, I don’t think we will be able to get enough support for that move.